Describe How Bacteria Develop Antibiotic Resistance
Despite targeting many critical pathways antibiotics have lost efficacy due to the evolution of resistance mechanisms in bacteria. Bacteria may evolve and learn to.
How Bacteria Build Resistance At The Cellular Level Online Public Health
Prescribers policymakers and researchers are.
. What you need to know Medically reviewed by Daniel Murrell MD Antimicrobial resistance AMR or drug resistance develops when bacteria viruses or fungi stop responding. Dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes is an ecological and public health concern. This study discusses the impact of antibiotic resistance as a persistent global health threat and highlights efforts to improve this complex problem.
Overuse of antibiotics has increased resistance in MRSA and other infectious bacteria because resistance genes the genes that code for resistance can be passed from bacteria to bacteria. There are three Domains and six Kingdoms under this system. 182425 It is hypothesized that antibiotics evolved as weapons for biological warfare between bacteria which means that resistance has been developing for.
Bacteria can also contain plasmids small extra-chromosomal molecules of DNA that may contain genes for various useful functions such as antibiotic resistance metabolic capabilities or various virulence factors. Transferring antibiotic resistance genes can contribute to the spread of illness in humans. In nature microbes are constantly evolving in order to overcome the antimicrobial compounds produced by other microorganisms.
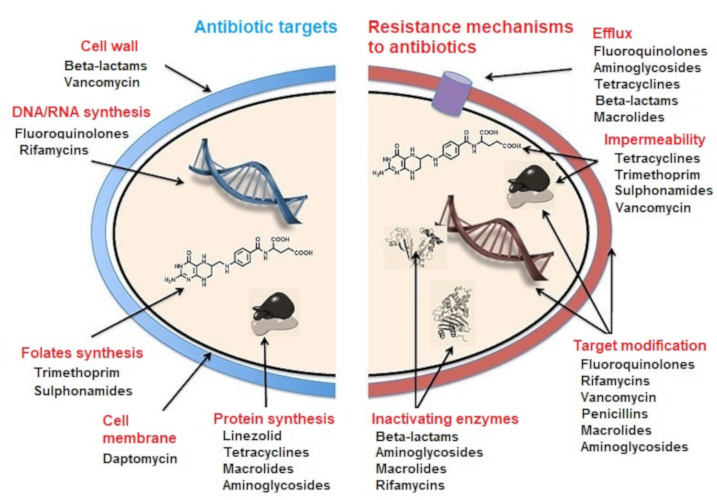
Pneumoniae the acquisition of a so-called extended-spectrum beta-lactamase EBSL and in the case of. Antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria evolve to evade the effect of antibiotics through multiple different mechanisms. Certain bacteria are able to neutralize an antibiotic by altering its component to render it ineffective.
Bacteria genomes usually encode a few hundred to a few thousand genes. This group is notoriously known to develop antibiotic resistance. Antibiotic resistance is an increasing concern and you may be at a higher risk if you take antibiotics when they arent necessary.
Some but not all strains of. Now the consensus of the scientific community is creating a level called the Domain above the Kingdom. The assumption is that a first-line antibiotic for which there is a prevalence of resistance greater than 200 should not be considered to be as effective as another first-line agent with minimal resistance and only a few case reports of clinical resistance.
Human development of antimicrobial drugs. Antibiotic-resistant bacteria especially those that are resistant to multiple drugs pose a major threat to health globally. In the evaluation we included the availability of paediatric and oral formulations which would have a substantial.
Describe the different mechanisms of antimicrobial drug resistance. Gut microbiota are the microorganisms including bacteria and archaea that live in the digestive tracts of vertebrates including humans and of insects. Antimicrobial resistance is not a new phenomenon.
Describe how microorganisms develop or acquire drug resistance. Antibiotic Resistance Action Center Washington DC US The Antibiotic Resistance Action Center ARAC at the Milken Institute School of Public Health George Washington University commits to advancing knowledge of how antibiotic use in food animals impacts human health and to improving antibiotic prescribing in the urgent care sector. Others might be able to export the antibiotics out.
Common Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance. A deadly complication of MRSA is a deep infection necrotizing fasciitis which causes rapid spread and destruction of human tissues. In the old taxonomic system Bacteria belong to the Kingdom of Monera.
Alternative terms include gut flora an outdated term that technically refers to plants and gut microbiomeThe gastrointestinal metagenome sometimes defined as the microbiome is the aggregate of all the genomes of. Classification and types of bacteria. In the case of E.
Political agendas legislation development of therapies and educational initiatives are essential to mitigate the increasing rate of antibiotic resistance.
Emergence And Spread Of Antibiotic Resistance Part 2 React
What Is Antibiotic Resistance National Foundation For Infectious Diseases
Antibiotic Resistance Bioninja
Print Materials And Fact Sheets Antibiotic Resistance Cdc
Mutations And Selection Antibiotic Resistance React
How Bacteria Build Resistance At The Cellular Level Online Public Health
Evolution Of Plasmid Mediated Antibiotic Resistance In The Clinical Context Trends In Microbiology
Infographic How Antibiotic Resistance Can Spread Antimicrobial Resistance
What Is Antibiotic Resistance Facts Yourgenome Org
Antibiotic Resistance An Emerging Global Crisis
Antibiotic Resistance Health Navigator Nz
Antibiotics Antibiotic Resistance And Environment Encyclopedia Of The Environment
Antibiotic Resistance How It Works And How We Can Fight It With Crispr Diagnostics Mammoth Biosciences
How Bacteria Build Resistance At The Cellular Level Online Public Health
Schematic Diagram Highlighting The Antibiotic Resistance Mechanisms Download Scientific Diagram
What Should I Know About Antimicrobial Stewardship
Antibiotic Resistance Flow Chart In Bacteria And The Environment 36 Download Scientific Diagram
Antibiotic Resistance Biology For Majors Ii
Are You Aware About Pathogenic Biofilms And Their Involvement In Antibiotic Resistance Lallemand Pharma